
Medications should also be reviewed to make sure that they are not exacerbating the underlying condition or contributing to the development of symptoms. Strict adherence to dietary modifications can also be helpful.

Antibiotics remain the mainstay of therapy and have been demonstrated to be effective in restoring normal bacterial balance, reducing mucosal inflammation and eliminating associated symptoms. Treatment of SIBO is aimed at reducing the bacterial overload, correcting the underlying cause, and providing nutritional support including supplementation of any vitamin or mineral deficiencies that may be necessary. How Is Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Treated? Players, stakeholders, and other participants in the global Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) Diagnostics market will be able to gain the upper hand as they use the report as a powerful resource. It has been suggested that the disordered motility and chronic diarrhea which can occur in some patients with IBS may predispose to SIBO. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) Diagnostics market is segmented by players, region (country), by Type and by Application. While there remains debate within the scientific community, some studies have demonstrated that a significantly higher percentage of patients who met the Rome I criteria for IBS also tested positive on SIBO breath testing as compared to healthy controls. There is a great deal of interest in better understanding the relationship between IBS and SIBO. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a disorder whereby bacteria excessively grows in the small intestine it is not a severe disorder and does.
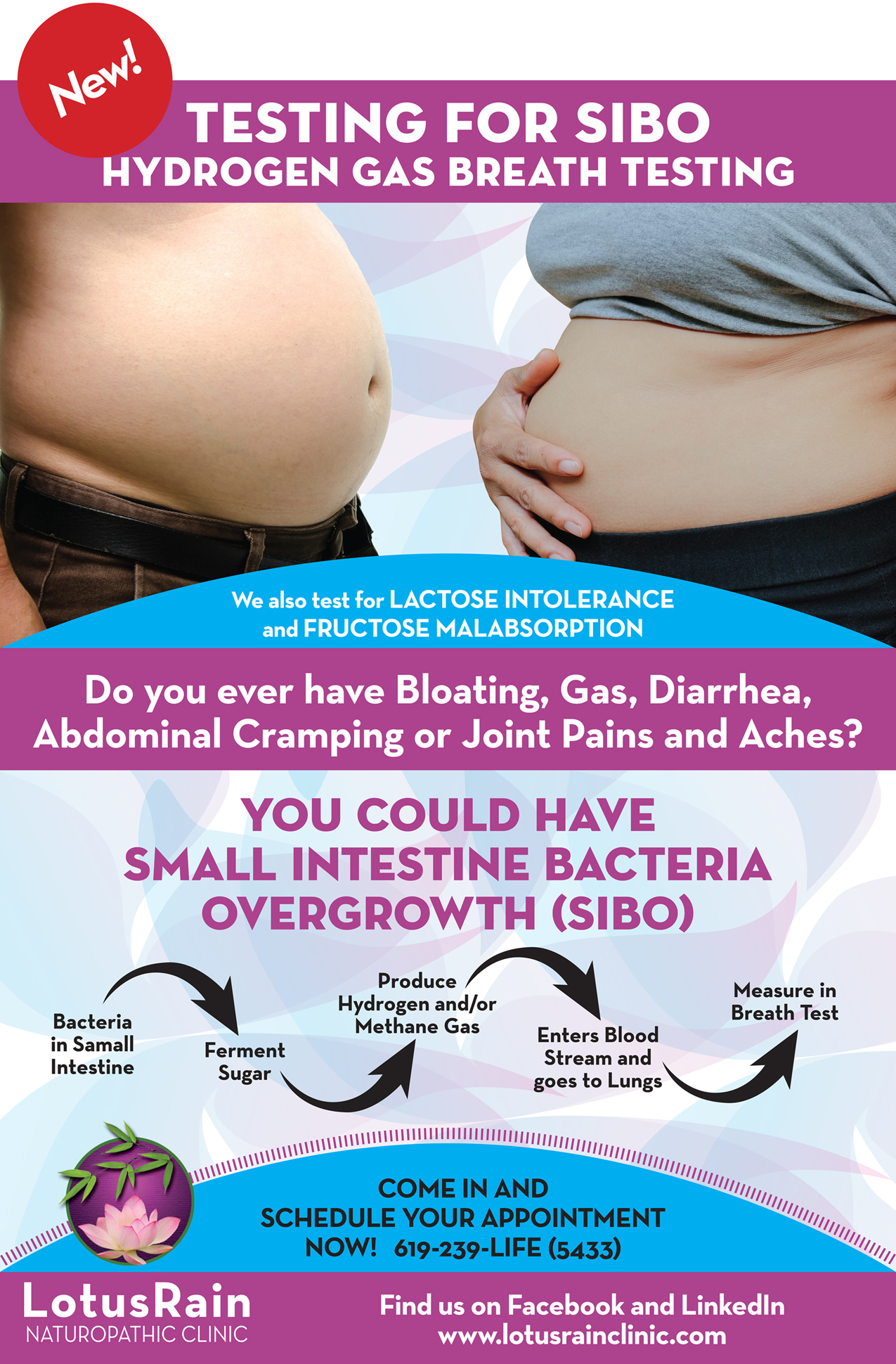
The symptoms of SIBO are often indistinguishable from those attributed to Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). What Is The Relationship Between SIBO and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? The severity of these symptoms varies from mild to severe and is likely influenced by the degree of overgrowth and extent of mucosal inflammation.Ĭonstant use of antibiotics, chronic alcohol use, and celiac disease are all leading factors that could lead to the development of SIBO. Malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies, including vitamin B12, may also be found in patients with SIBO. The symptoms of SIBO are non-specific and include bloating, abdominal pain/ distension, diarrhea, flatulence, fatigue, weakness, and weight loss. Use of antibiotics, diminished gastric acid secretion, small intestinal dysmotility (including in patients with long-standing diabetes or celiac disease), history of chronic diarrhea, chronic alcohol use, and anatomical abnormalities of the GI tract are some of the predisposing factors that may increase the likelihood of developing SIBO. If you have SIBO, discuss food and dietary options with one of our experienced diet and nutrition providers. Foods that trigger bacterial growth such as sugar, refined carbohydrates, and lactose should be reduced or eliminated in the SIBO diet. Dietary changes are necessary for many SIBO patients. Studies have demonstrated reversal of mucosal damage after treatment for SIBO. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Diet. Once present, it has been suggested that this imbalance of bacteria may induce an inflammatory response in the small intestinal mucosa which produces many of the symptoms associated with this condition.
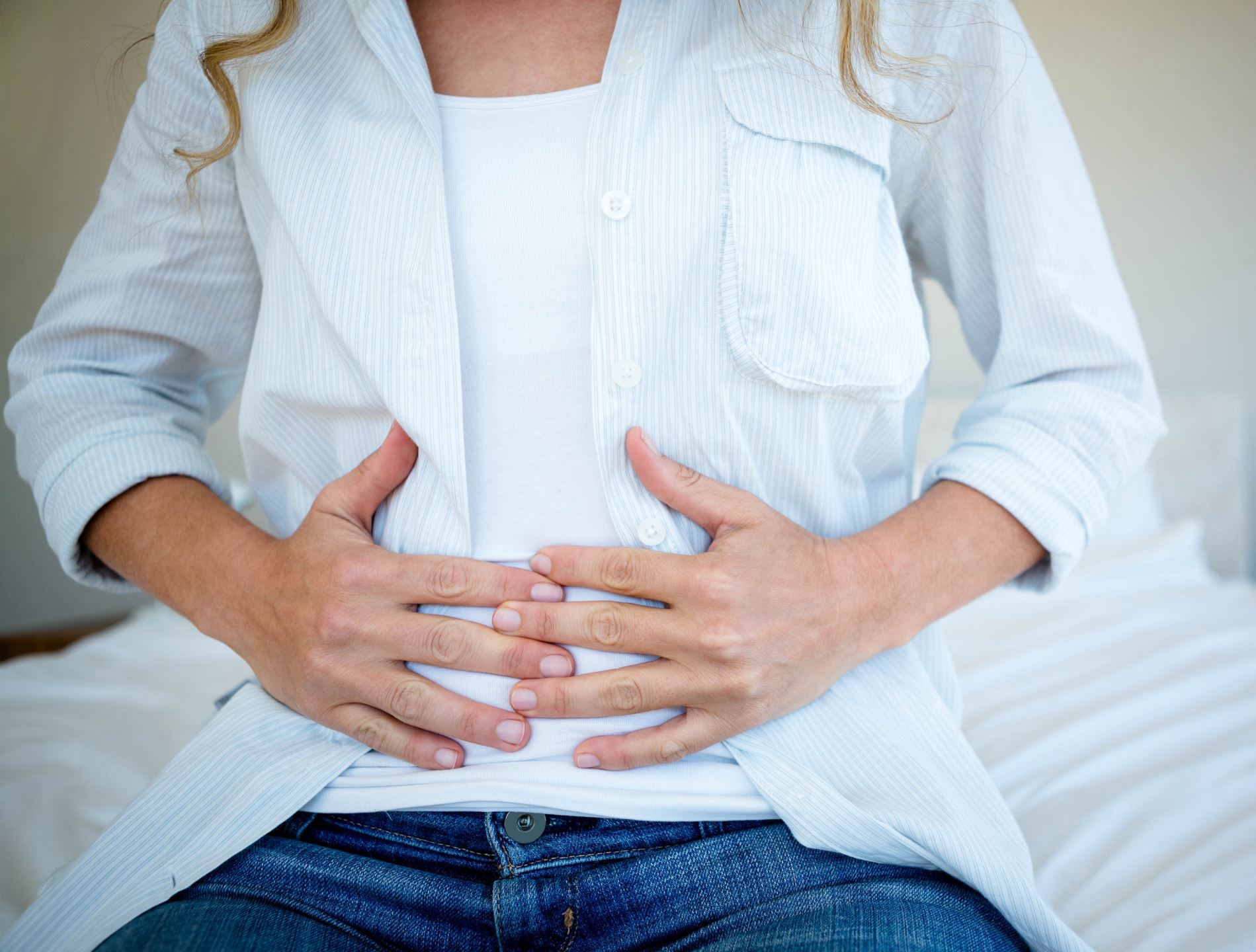

Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is defined as an excess of bacteria in the small intestine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
